이번 2학기 개발에서는 기존 카카오 로그인에 추가로 네이버 로그인과 구글 로그인을 추가하게 되었다.
카카오 로그인과 구글 로그인도 글을 작성하겠지만, 우선 네이버 로그인부터 작성을 해보려고 한다.
각각의 Oauth에서는 사용할 기능이 토큰 받아오기, 사용자 정보 받아오기 이렇게 2가지이기 때문에 인터페이스를 만들고 해당 인터페이스를 구현하는 방법으로 각각의 Oauth 로그인을 만들었다.
우선 작성한 인터페이스이다.
interface OauthService {
fun getOauth(code: String, isRemote: Boolean): Oauth
fun getAccessToken(code: String, isRemote: Boolean): String
}
redirect_uri를 원격서버, 로컬서버 이렇게 2개 연결하고 싶었기 때문에 그것을 결정하기 위한 isRemote 파라미터를 추가하였다.
그리고 Oauth에서 정보를 받아와 사용자의 정보를 구별하기 위한 Oauth data class를 사용하였다.
사용한 Oauth data class는 다음과 같다.
@Entity
@Table(
indexes = [
Index(name = "idx_type_id", columnList = "oauthType, oauthId")
]
)
data class Oauth(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
var id: Int?,
@ManyToOne
var user: User?,
@Column(length = 100)
var oauthId: String,
@Enumerated(EnumType.ORDINAL)
var oauthType: OauthTypeEnum
)
그러면 이제 네이버 Oauth를 통해서 oauthId를 받아오도록 해보자.
우선 여기에서 애플리케이션을 등록해야 한다.
https://developers.naver.com/main/
NAVER Developers
네이버 오픈 API들을 활용해 개발자들이 다양한 애플리케이션을 개발할 수 있도록 API 가이드와 SDK를 제공합니다. 제공중인 오픈 API에는 네이버 로그인, 검색, 단축URL, 캡차를 비롯 기계번역, 음
developers.naver.com
그리고 토큰을 받아올 수 있도록 redirect_uri를 지정해준다.
우선 로컬에서 사용하기 때문에, http://localhost:8080/api/auth/naver-login으로 만들어줬다.
이 주소는 나중에 서비스가 배포된다면 변경해주거나 추가해주어야 한다.
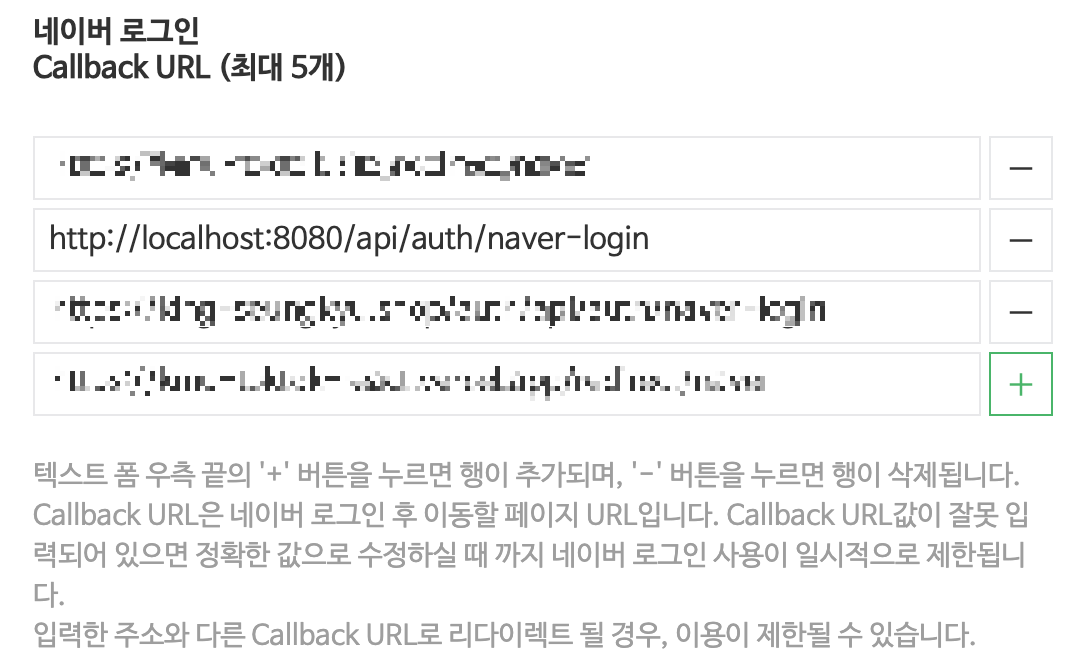
우선 Controller이다.
@GetMapping("/naver-login")
@Operation(summary = "네이버 로그인 API")
@Parameters(
Parameter(name = "code", description = "네이버 로그인 code")
)
fun getNaverLogin(
@RequestParam code: String
): ResponseEntity<CoBoResponseDto<GetAuthLoginRes>>{
return authService.getNaverLogin(code)
}이렇게 그냥 Parameter로 코드만 가져오면 된다.
- AccessToken 받아오기
private final val naverAccessTokenServer = "https://nid.naver.com/oauth2.0/token"
override fun getAccessToken(code: String, isRemote: Boolean): String {
val restTemplate = RestTemplate()
val httpHeaders = HttpHeaders()
httpHeaders.add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8")
val httpBody = LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String>()
httpBody.add("client_id", clientId)
httpBody.add("client_secret", clientSecret)
httpBody.add("code", code)
return restTemplate.postForObject(naverAccessTokenServer, this.getHttpEntity(httpBody), NaverAccessToken::class.java)?.accessToken ?: ""
}
fun getHttpEntity(httpBody: LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String>): HttpEntity<LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String>> {
val httpHeaders = HttpHeaders()
httpHeaders.add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8")
httpBody.add("grant_type", "authorization_code")
return HttpEntity(httpBody, httpHeaders)
}
private data class NaverAccessToken(
@JsonProperty("access_token") val accessToken: String,
@JsonProperty("state") val state: String?,
@JsonProperty("error") val error: String?,
@JsonProperty("error_description") val errorDescription: String?
)
RestTemplate를 통해 작성했다.
https://nid.naver.com/oauth2.0/token
해당 주소로 POST를 사용해
client_id, client_secret, code를 넣어서 요청하면 된다.
응답받는 json은 아래와 같다.
당연히 client_id, client_secret은 환경변수에 넣어두고 가져오면 된다.
이렇게 해당 사용자의 AccessToken을 받아오게 되었다.
- 사용자 정보 가져오기
이제 사용자의 고유 Id를 가져오자.
응답받은 AccessToken을 그대로 넣어서 요청하면 끝난다.
https://developers.naver.com/docs/login/profile/profile.md
네이버 회원 프로필 조회 API 명세 - LOGIN
네이버 회원 프로필 조회 API 명세 NAVER Developers - 네이버 로그인 회원 프로필 조회 가이드 네이버 로그인을 통해 인증받은 받고 정보 제공에 동의한 회원에 대해 회원 메일 주소, 별명, 프로필 사
developers.naver.com
private final val naverUserInfoServer = "https://openapi.naver.com/v1/nid/me"
override fun getOauth(code: String, isRemote: Boolean): Oauth {
val accessToken = getAccessToken(code, isRemote)
val restTemplate = RestTemplate()
val naverUserInfo = restTemplate.exchange(
RequestEntity<Any>(this.getHttpHeadersWithAuthorization(accessToken), HttpMethod.GET, URI.create(naverUserInfoServer)),
NaverUserInfo::class.java
).body
val naverUserId = naverUserInfo?.response?.id ?: ""
return this.getOauthFromOauthIdAndOauthType(
oauthId = naverUserId,
oauthTypeEnum = OauthTypeEnum.NAVER,
accessToken = accessToken)
}
fun getHttpHeadersWithAuthorization(accessToken: String): HttpHeaders{
val httpHeaders = HttpHeaders()
httpHeaders.add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8")
httpHeaders.add("Authorization", "Bearer $accessToken")
return httpHeaders
}
private data class NaverUserInfo(
@JsonProperty("resultcode") val resultCode: String,
@JsonProperty("message") val message: String,
@JsonProperty("response") val response: Response,
)
private data class Response(
@JsonProperty("id") val id: String,
@JsonProperty("nickname") val nickname: String?,
@JsonProperty("name") val name: String?,
@JsonProperty("email") val email: String?,
@JsonProperty("gender") val gender: String?,
@JsonProperty("age") val age: String?,
@JsonProperty("birthday") val birthday: String?,
@JsonProperty("profile_image") val profileImage: String?,
@JsonProperty("birthyear") val birthyear: String?,
@JsonProperty("mobile") val mobile: String?
)
하지만 이번은 Post가 아니라 Get이기 때문에 다른 방법을 사용한다.
저렇게 헤더에 Bearer로 토큰만 넣어주면 응답값이 나온다.
응답의 결과는 아래의 data class와 같지만, 어차피 id만 사용하기 때문에 id만 가져오도록 만들었다.
이렇게해서 네이버 로그인으로 로그인한 사용자를 고유번호를 통해 식별할 수 있게 되었다.
아래는 사용한 전체 코드이다.
package cobo.auth.service.oauth.impl
import cobo.auth.data.entity.Oauth
import cobo.auth.data.enums.OauthTypeEnum
import cobo.auth.repository.OauthRepository
import cobo.auth.service.oauth.OauthService
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod
import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate
import java.net.URI
@Service
class NaverOauthServiceImpl(
@Value("\${naver.auth.client_id}")
private val clientId: String,
@Value("\${naver.auth.client_secret}")
private val clientSecret: String,
private val oauthRepository: OauthRepository
): OauthService, OauthServiceImpl(oauthRepository) {
private final val naverAccessTokenServer = "https://nid.naver.com/oauth2.0/token"
private final val naverUserInfoServer = "https://openapi.naver.com/v1/nid/me"
override fun getOauth(code: String, isRemote: Boolean): Oauth {
val accessToken = getAccessToken(code, isRemote)
val restTemplate = RestTemplate()
val naverUserInfo = restTemplate.exchange(
RequestEntity<Any>(this.getHttpHeadersWithAuthorization(accessToken), HttpMethod.GET, URI.create(naverUserInfoServer)),
NaverUserInfo::class.java
).body
val naverUserId = naverUserInfo?.response?.id ?: ""
return this.getOauthFromOauthIdAndOauthType(
oauthId = naverUserId,
oauthTypeEnum = OauthTypeEnum.NAVER,
accessToken = accessToken)
}
override fun getAccessToken(code: String, isRemote: Boolean): String {
val restTemplate = RestTemplate()
val httpHeaders = HttpHeaders()
httpHeaders.add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8")
val httpBody = LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String>()
httpBody.add("client_id", clientId)
httpBody.add("client_secret", clientSecret)
httpBody.add("code", code)
return restTemplate.postForObject(naverAccessTokenServer, this.getHttpEntity(httpBody), NaverAccessToken::class.java)?.accessToken ?: ""
}
private data class NaverAccessToken(
@JsonProperty("access_token") val accessToken: String,
@JsonProperty("state") val state: String?,
@JsonProperty("error") val error: String?,
@JsonProperty("error_description") val errorDescription: String?
)
private data class NaverUserInfo(
@JsonProperty("resultcode") val resultCode: String,
@JsonProperty("message") val message: String,
@JsonProperty("response") val response: Response,
)
private data class Response(
@JsonProperty("id") val id: String,
@JsonProperty("nickname") val nickname: String?,
@JsonProperty("name") val name: String?,
@JsonProperty("email") val email: String?,
@JsonProperty("gender") val gender: String?,
@JsonProperty("age") val age: String?,
@JsonProperty("birthday") val birthday: String?,
@JsonProperty("profile_image") val profileImage: String?,
@JsonProperty("birthyear") val birthyear: String?,
@JsonProperty("mobile") val mobile: String?
)
}
package cobo.auth.service.oauth.impl
import cobo.auth.data.entity.Oauth
import cobo.auth.data.enums.OauthTypeEnum
import cobo.auth.repository.OauthRepository
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture
open class OauthServiceImpl(
private val oauthRepository: OauthRepository
) {
fun getHttpEntity(httpBody: LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String>): HttpEntity<LinkedMultiValueMap<String, String>> {
val httpHeaders = HttpHeaders()
httpHeaders.add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8")
httpBody.add("grant_type", "authorization_code")
return HttpEntity(httpBody, httpHeaders)
}
fun getHttpHeadersWithAuthorization(accessToken: String): HttpHeaders{
val httpHeaders = HttpHeaders()
httpHeaders.add("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=utf-8")
httpHeaders.add("Authorization", "Bearer $accessToken")
return httpHeaders
}
fun getOauthFromOauthIdAndOauthType(oauthId: String, oauthTypeEnum: OauthTypeEnum, accessToken: String): Oauth {
val optionalOauth = oauthRepository.findByOauthIdAndOauthType(oauthId, oauthTypeEnum)
if (optionalOauth.isPresent) {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync{
optionalOauth.get()
}.thenApply {
oauthRepository.save(it)
}
return optionalOauth.get()
}
else{
return oauthRepository.save(Oauth(
id = null,
user = null,
oauthId = oauthId,
oauthType = oauthTypeEnum
))
}
}
}'크무톡톡 프로젝트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 카카오 Oauth 로그인, SpringBoot (0) | 2024.07.25 |
|---|---|
| 구글 Oauth 로그인, SpringBoot (0) | 2024.07.24 |
| Nginx로 Swagger Proxy_pass (1) | 2024.07.22 |
| CompletableFuture 적용으로 성능 튜닝 (0) | 2024.03.09 |
| Springboot와 DialogFlow 연동 - API (0) | 2024.01.17 |